- Contributions by industrial experts with engineers in mind
- Focused on specialty-chemical material applications and selection
Knowledge Center
Q&A Tutorial on the Adhesive Sealant Selection Process

Adhesive Sealants Selection Q&A
Adhesive sealants are both industrial adhesives and industrial sealants. These liquid products bond substrates together and seal-out the environment by preventing contaminants from entering or escaping from an assembly. Adhesive sealants remain flexible enough to support substrate movement and are available in different types for various applications.
For design engineers who want to know more about adhesive sealants, this Q&A series from Gluespec® provides answers to frequently asked questions (FAQs). In addition to this FAQ about adhesive sealant selection, there is an introductory FAQ and an adhesive sealant type FAQ.
Q: When should you select polyurethane adhesive sealants?
Polyurethane adhesive sealants provide superior bond strength but lack the high-temperature and UV resistance that some applications require. However, their range of service temperatures is suitable for many industrial applications. Plus, the ease with which they accept paint supports their use as a UV protective coating for outdoor applications, including those in marine environments. Polyurethane adhesive sealants are especially good when submersion in water is an aspect of the intended use.
Q: When should you select silicone adhesive sealants?
Silicone adhesive sealants are used in applications with service temperatures above 120°C and have good UV resistance. Silicones are difficult to paint, however, which is why some engineers choose polyurethane or SMP adhesive sealants instead. Although silicone adhesive sealants can’t match polyurethane or SMP products in terms of bond strength, silicones come in formulations with a UL 94 V-0 flame rating and MIL Spec approval. That’s important for automotive and consumer electronics.
Q: When should you select butyl adhesive sealants?
Butyl adhesive sealants provide excellent resistance to UV, moisture, and aging. These elastomer-based products are used when a softer durometer, or lower level of hardness, is required and the service temperature is 120°C or below. Butyl adhesive sealants are not a good choice if resistance to acids is required; however, their ability to be painted is a plus in some applications. Unlike other types of sealants, butyl does not require curing. This supports shorter cycle times and greater manufacturing efficiency.
Q: When you should select polysulfide adhesive sealants?
Polysulfide adhesive sealants combine high and low temperature resistance with high physical strength, exceptional chemical resistance, and long-term resistance to many petroleum products. These products also provide resistance to shock, vibration, impact, and thermal cycling. Polysulfide adhesive sealants are often used in harsh aerospace environments and for lining industrial tanks. Specific applications include window/canopy sealing, fuel tank sealing/fuel resistance, and high temperature use.
Q: When should you select silane modified polymer (SMP) adhesive sealants?
SMP adhesive sealants are recommended when a combination of bond strength, environmental resistance, and UV resistance are required. They are suitable for temperatures up 120°C and have applications that range from panel bonding to installing floors and windows. When bond strength is critical, either an SMP adhesive sealant or a polyurethane product is the best choice. With SMP products, however, high-temperature and UV resistance are provided along with bond strength.
Q: Can you select adhesive sealants based on product specifications alone?
Manufacturers of adhesive sealants generally provide a standard set of product specifications; however, they may not use the same tests to determine a specification’s values. Therefore, it is important to use listed specifications as a general guide, especially if an industry-standard test from an organization such as ASTM is not provided.
Q: What are some of the most important specifications for adhesive sealants?
Tensile lap shear, dyne testing, and ultimate adhesion can all provide useful points of comparison for adhesive sealants.
- -Tensile lap shear measures an adhesive bond’s shear strength where two members are bonded together in a lap joint and then pulled at both ends until the joint fails in shear.
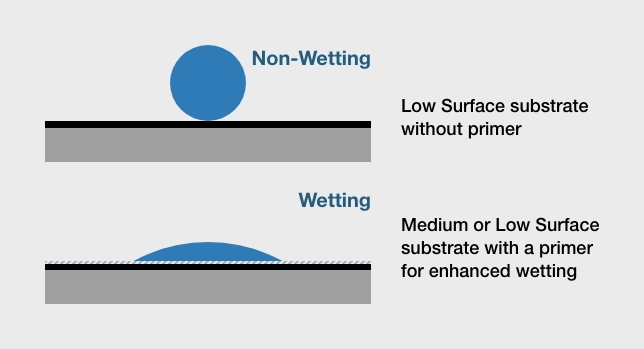
- -Dyne testing measures surface wettability or adhesion and is used to determine surface energy.
- -Ultimate adhesion occurs after the application and full cure of an adhesive material.
Adherence to U.S. military or other specifications may be required for some projects.
Q: What about product selection for different types of applications?
Adhesive sealants are used in applications ranging from printed circuit boards (PCBs) and light emitting diodes (LEDs) to smart meters, power tools, and e-mobility solutions. They’re also used in electrical leads, electronics and electronic equipment, liquid crystal display (LCD) modules, and power supplies.
Q: What else do engineers need to know?
In addition to the information in this FAQ about adhesive sealant selection, engineers need to know about adhesive sealant types. It’s also a good idea to familiarize yourself with Gluespec’s introductory FAQ to this category of products.